Difference between revisions of "OPP"
(→Processor Boards) |
(→Processor Boards) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
=== Processor Boards === | === Processor Boards === | ||
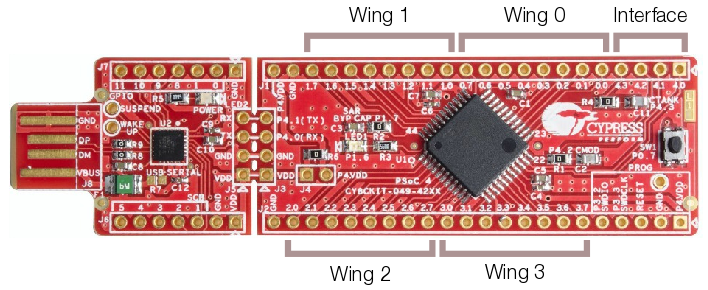
| − | The | + | The ''Processor'' board can control up to four ''Wing'' boards controlling solenoids, incandescent lamps, or allowing input for switches. The ''Wing'' boards themselves can be combined in any configuration, so a single ''Processor'' board can support up to 16 solenoids, 32 switch inputs or 32 lamps. Each ''Wing'' board uses eight pins while the ''Interface'' board uses four. |
| + | |||
| + | All other pins are unused, except on the first board in the chain where the USB plug from the host controller is connected and is connected to the ''Interface'' board to provide power and serial connections for the other ''Processors'' in the chain. | ||
[[Image:opp-processor.png]] | [[Image:opp-processor.png]] | ||
| − | The | + | The ''Processor'' itself does not run game rules or other game logic - a ''Controller'' like [https://missionpinball.com/ Mission Pinball] running on a separate PC is still required to handle scoring and other game logic and to fire coils and light lamps as needed. The ''Processor'' simply provides the physical connection to playfield devices. |
=== Solenoid Wing === | === Solenoid Wing === | ||
The '''Solenoid''' wing uses [http://www.digikey.com/product-search/en?keywords=FQP13N06L FQP13N06L MOSFETs] to control up to four individual coils via a ''ground sink'' method, where the coils themselves are wired to the positive side of the high voltage power supply and the MOSFET provides a ground path when activated, firing the coil. | The '''Solenoid''' wing uses [http://www.digikey.com/product-search/en?keywords=FQP13N06L FQP13N06L MOSFETs] to control up to four individual coils via a ''ground sink'' method, where the coils themselves are wired to the positive side of the high voltage power supply and the MOSFET provides a ground path when activated, firing the coil. | ||
Revision as of 18:57, 17 August 2016
Open Pinball Project
The Open Pinball Project (OPP) was started in 2012 as a resource for pinball makers to have an inexpensive, fully open sourced project for controlling custom pinball machines. It is currently on a second generation design and has had a successful Kickstarter run of boards and components currently in the hands of makers all over the world.
Hardware
The OPP hardware is made up of three main components:
- The Processor board is a Cypress Semiconductor CY8CKIT-049-42XX PSoC prototyping board that can be purchased from Mouser or Digikey
- The Interface board allows communications between Processor boards via a custom serial communications protocol
- The Wing boards allow the control of solenoids, lamps, LEDs or input from switches
Processor Boards
The Processor board can control up to four Wing boards controlling solenoids, incandescent lamps, or allowing input for switches. The Wing boards themselves can be combined in any configuration, so a single Processor board can support up to 16 solenoids, 32 switch inputs or 32 lamps. Each Wing board uses eight pins while the Interface board uses four.
All other pins are unused, except on the first board in the chain where the USB plug from the host controller is connected and is connected to the Interface board to provide power and serial connections for the other Processors in the chain.
The Processor itself does not run game rules or other game logic - a Controller like Mission Pinball running on a separate PC is still required to handle scoring and other game logic and to fire coils and light lamps as needed. The Processor simply provides the physical connection to playfield devices.
Solenoid Wing
The Solenoid wing uses FQP13N06L MOSFETs to control up to four individual coils via a ground sink method, where the coils themselves are wired to the positive side of the high voltage power supply and the MOSFET provides a ground path when activated, firing the coil.