Controlling A Lamp Matrix
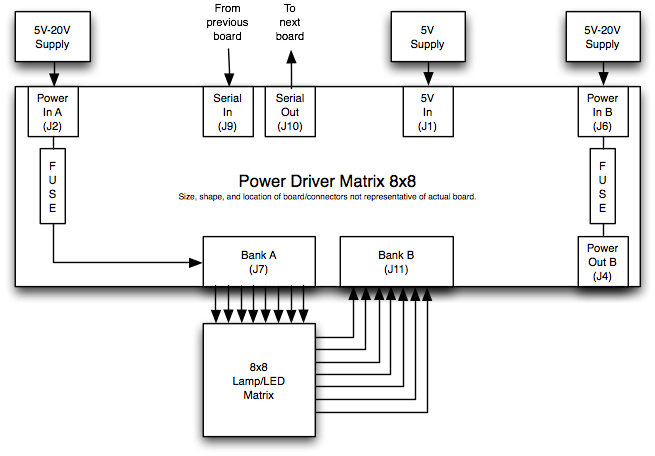
As shown in the diagram below, a single PD-8x8 board can control an 8x8 lamp matrix, providing individual control of 64 lamps (or LEDs).
The PD-8x8's source outputs (Bank A - J7) switch on/off your lamp voltage to the columns, and the PD-8x8's sink outputs (Bank B - J11) switch on/off ground to the rows. To turn a lamp on, both the voltage (source) and ground (sink) need to be on. When using a P-ROC as your main controller, the P-ROC tells the PD-8x8 to turn on each source output, one at a time. Each time a source output is on, the P-ROC tells the PD-8x8 to turn on ground for the active lamps in the corresponding rows. By cycling through each column fairly quickly, your eyes don't realize each lamp is only on for a maximum of 1/8th the cycle time.
Notice in the illustration that no power output connector is used on the PD-8x8 board. Power is sourced to each lamp column through J7.
Lamp Voltage
PD-8x8 boards can source between 5V and 20V DC. The voltage on your matrix is determined by what you connect to the PD-8x8 power input connectors (J2 and J6).
Note PD-8x8's will only work with DC voltage, not AC.
Matrix Sizes
A single PD-8x8 board can control an 8x8 lamp matrix.
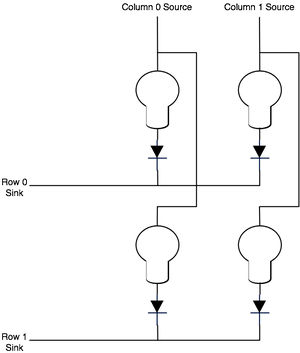
To control a smaller matrix, don't use all of the outputs. For example, if you want a 2x2 matrix, you would connect only 2 columns (source) and 2 rows (sink) as shown in the following image:
To control a larger matrix, you can use additional 'sink' banks, either by using a Bank B from another PD-8x8 or by using either bank from a PD-16. Theoretically, you could add as many additional sink banks as you need, though the P-ROC can only automatically control 224 matrix elements (assuming no other features, like coils, are under the P-ROC's control). To control more than 224 matrix elements, you'll have to issue the matrix column and row commands in software.
Another way to control a larger matrix is to use multiple PD-8x8 source banks, though the P-ROC can automatically control only 2 lamp matrix source banks automatically. To control more than 2 lamp matrix source banks, you'll have to issue the matrix column and row commands in software.
Diodes
Due to the wiring configuration in a matrix, it's theoretically possible for current flowing through one 'on' lamp to leak through an 'off' lamp in the same row. This is typically avoided with the use of a diode. If a diode is wired in series with each lamp, as shown in the 2x2 matrix image above, current flowing through another lamp can't leak back through.
LED's ARE diodes; so it's generally not necessary to use a separate diode for each LED in an LED matrix. However, some LED bulbs are designed to be bi-directional, allowing the bulb to be plugged in in either orientation. Since current can flow through these bi-directional LED bulbs in either direction, a separate diode is necessary to avoid having current leak through 'off' LEDs, which would result in ghosting.